Cancer is an abnormal proliferative cell growth that can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can be classified as benign ( noncancerous and spreading ) and malignant tumor.
Benign tumors are tumors that do not spread or leave its tissue of origin. They stay in the tissue where they originated, while malignant tumors are tumors that spread to other parts of the body. They can leave their tissue of origin and transfer to somewhere else. Malignant tumors are named after their tissue of origin, not after the destination tissue.
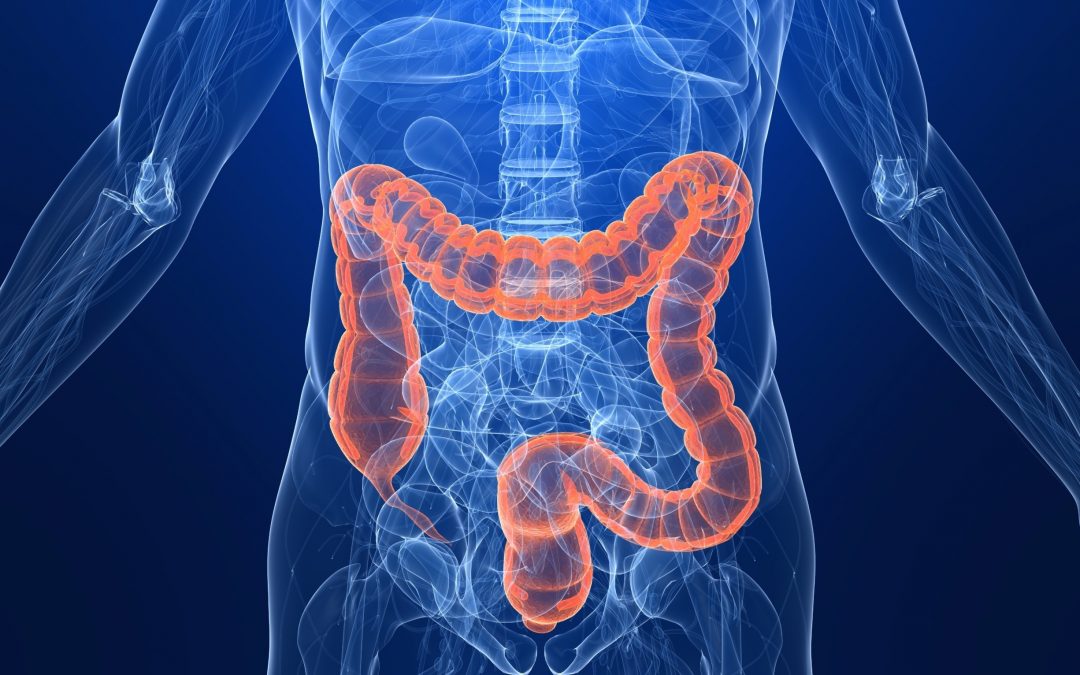
Colon cancer is a malignant tumor also known as bowel or colorectal cancer., This cancer affects the colon or rectum as the name implies and is the third leading cause of cancer in both genders in the United State of America. Because, of its epidemiological importance, a lot of awareness has been created for early diagnosis and screening. Colon cancer often metastasizes to the lungs, liver, and the peritoneum.
Top Ten Reasons to Have a Colon Cancer Screening
- Prevention of colorectal cancer: Colonoscopy screening helps in the early detection of polyps that develops into colorectal cancer.
- It helps in early detection of colorectal cancer
- It saves lives through early detection of the polyps
- It provides varieties of screening methods and options to pick from.
- Proper spacing between screen, by ensuring that is done only once every ten years.
- Good funding by avoiding co-pay payment and fund sourcing.
- Generation saver: early detection can help save your kids and grand children, you can do the m a favor they would be forever grateful for by having your screening early.
- It helps in saving money for expensive treatments if it is detected earlier
- It increases quality of life, which would be worsened if disease is detected late
- It gives the opportunity to spend more time with our loved ones; the early screen would make you plan your life, and help your loved ones know your health status.
Risk Factors for Having Colon Cancer

- Lifestyle choices: these include poor dietary choices, excessive alcohol intake, smoking, obesity and living a sedentary way of life.
- Dietary factors: it has been discovered that excessive intake of red, processed meat can increase the chances of having colon cancer.
- Inflammatory diseases: people with the previous history of various inflammatory diseases such as Chron’s disease and ulcerative colitis are more prone to having colon cancer.
- Genetic disease: Individuals with inherited genetic diseases or family history of familiar adenomatous polyposis(FAP), colon polyps, colorectal cancer and hereditary non- polyposis colon cancer are prone to having colon cancer.
- Age: The chances of having colorectal cancer increase with age, the older you get, the more you should take your screening seriously. It is more common in people older than 5o years.
- Race: The most susceptible races are the African- American and American-Indian races.
- Underlying conditions: People with a previous underlying endocrine disease such as diabetes, or previous cancer
- Dehydration: It increases the risk of having cancer of the colon
- Infection: Some streptococcus bacteria could increase the risk of having cancer of the colon, examples of such bacteria include Streptococcus gallolyticos, which is a gram-positive
- Previous history: Previous or family history of colon cancer can predispose a patient to have colon cancer. Prior chemotherapy treatment or exposure to radiation can also increase the chances of having cancer.
Signs and Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is called the silent disease because it can often be asymptomatic. That is why medical doctors advise people to do the early screening.Early screen and early detection is the key to fighting and eliminating this disease.

The Common Signs and Symptoms of Colon Cancer
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: these include nausea, cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, bloatedness, postprandial fullness, and feeling of incomplete evacuation.
- Cachexia: This is pathognomic for all types of cancer.
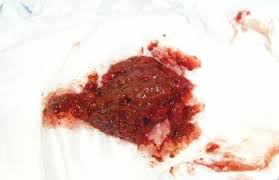
- Rectal bleeding: This is indicated by red or dark blood in the stool. This bleeding can lead to anemia of the iron deficiency type. When there is excessive blood loss, the patient will express fatigue and tiredness.
- Bowel consistency changes: There would be a change in bowel consistency. This includes changes in appearance, volume, and texture of the stool.
- Dyspnea: There can be difficulty in breathing especially when there is the presence of metastases.
The location of cancer can determine the signs and symptoms present. If a cancerous cell is located on the left side of the colon, it can lead to partial or total obstruction. This blockage can cause various gastro intestinal symptoms such as nausea, and vomiting. If the cancerous cell is present on the right side of the colon, it can lead to anemia which is responsible for the weakness, fatigue, and tiredness experienced by colon cancer patient.
Despite all the following symptoms stated above the most frequently asked question which is:
Does Blood in Your Stool Mean You Have Colon Cancer
This question can be likened to asking does a bad football player makes the whole team a bad team. In medicine, diagnosis is made based on combination of signs, symptoms, and test results, Blood in the stool(hematochezia) due to rectal bleeding is a principal sign of colon cancer but is not enough to make a diagnosis. Hematochezia can be likened to the captain of a football team. Although he is important, not only he makes up the team. Hematochezia is a cardinal sign but is not enough to make colon cancer diagnosis. However, hematochezia is caused by different etiologies apart from colon cancer. These different etiologies include fissures in the anal canal, hemorrhoids, Merkel’s diverticulum, ulcer, diverticulosis, colitis, and angiodysplasia.
When to See a Doctor
Contact your doctor when you notice blood in your stool or any of the above symptoms above to confirm the diagnosis or rule out colon cancer. Colon cancer can appear asymptomatic, so when you notice symptoms, contact your doctor as soon as possible.The sooner you detect it, the better the prognosis.
Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy: this involves the insertion of a thin tube into the colon for viewing purpose. The result gotten from the colonoscopy is sent to the pathologist for biopsy, to identify the causative organism.
- Sigmoidoscopy: This involves using a smaller tube compared to colonoscopy to view the sigmoid colon, which is present on the left-hand side of the colon.
- CT SCAN: This is used to detect the degree of metastasis of the colon cancer because the colon cancer can metastasize to the lung, liver or peritoneum.
- Positron emission tomography scan (PET SCAN): This is used to detect the metabolic activity of the cancerous cells and help to check the spread of cancerous c cells to the lymph nodes and other organs.
- Blood test: This can help in detection of a tumor marker called carcinoma-embryogenic antigen(CEA),. This tumor marker can be an indication for colon cancer. However, this marker is not specific because some colon cancer patients might be asymptomatic or without the presence of tumor markers in their blood. This tumor marker can also be seen in non- cancerous patients, especially smokers. The presence of this tumor marker is not a particular diagnosis criterion for colon cancer. However, it is effective when combined with other signs, symptoms, and laboratory test results.
- Barium enema: This is a colonic x-ray that involves the injection of a contrast fluid enema into the rectum for proper visualization of the rectum. This helps in detecting cancerous cell in the colon.
Due to all the information and awareness programs on the internet and social media, many people are confused, scared, and ask this frequent question which is:
Who Should Have a Colonoscopy and How Often Should it Be Done
Individuals with any suspect symptoms of colon cancer or high risk of having colon cancer should undergo colonoscopy. However, colonoscopy can also be used as a form of screening for asymptomatic patients.
The frequency of doing colonoscopy depends on your risk of having colon cancer. People with an average risk of colon cancer are advised to do colonoscopy every ten years starting at the age of 5o, while individuals with high risk and family history should start at an earlier age.
Colon Cancer Screening
Screening is used for detecting cancerous and precancerous cells in asymptomatic individuals and in people with an average risk of developing this diseases. In colon cancer diagnosed a patient, diagnosis rather than screening is performed on them. Screening is carried out to achieve early detection because early detection can help increase the prognosis of the disease. Screening is advisable to be done from the age of 50, in asymptomatic patients with average risk of colon cancer. In patients with a high risk of colon cancer such as family history, it is advisable to start the screening at the age of 45. Don’t wait till it is too late, or the symptoms pushes you to the clinic. Start your screening now.
Types of Screening for Colon Cancer
- Fecal occult blood testing(FOBT): this involves the detection of hematochezia(blood in stool) is used for detecting even the smallest amount of blood in the stool microscopically.there are two different types of FOBT:
- Guaiac fecal occult blood test: this involves the detection of hematochezia by collecting three consecutive stools and testing them on a special card with a chemical.
- Immunochemical test: This is a more sensitive and preferable test to guaiac test, that uses antibodies to detect the presence of blood in a stool A special solution containing antibodies is added to the stool to detect the presence of blood.
- Irrespective of the type of fecal occult blood test used.Positive test for a fecal occult blood test only indicates 30-45% of having polyps and 3-5 % of having colon cancer. This alone is not sufficient to make a diagnosis., Because other condition can give a positive fecal occult blood test, and a colon cancer patient could have an adverse result for
- Flexible colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy: This involves inserting a flexible tube into the sigmoid colon and large intestine respectively for viewing purposes. It is advisable for people with high risk of colon cancer and family history to do this before the age of 50. In a patient with a history of cancer in their first relatives, it is better to do colonoscopy ten years earlier before, it is detected in the family member. All these rules are to ensure early detection which helps in increasing the prognosis.
- Virtual colonoscopy: this is also called CT colonography, It involves the use of CT scan at low dose radiation to view the colon, It is essential to give the patient laxatives before this procedure is done, It is useful in detecting polyps greater than one centimeter. It is only used for detection and not removal of polyps
- DNA test for stool: this is done to detect the presence of DNA cells or hemoglobin in the stool, a positive result in the test is not enough to make a diagnosis of colon cancer.
Having the right knowledge about different types of screening for colon cancer is not sufficient, but applying this knowledge is the key to fighting this disease. Screening is essential for early detection and a better in prognosis.
Colon Cancer on the Rise in Young People- Should You Be Screened?
Despite the age prevalence and age group affected by colon cancer, it is better to do your screening early, because Colon Cancer on the Rise in Young People. Early detection is the key to early treatment and a good prognosis. It has been discovered that people that detected their colorectal cancer earlier in life can live long after surgery. The later the discovery of cancer, the worse the prognosis will become.
Due to different factors such as time of detection, family history, the degree of risk of colon cancer. The chances of surviving colon cancer vary and depend on the stage of cancer:
- Stage 1 patient has a survival rate of 80-95%
- Stage 2 patient has 55-80% chance of surviving
- Stage 3 patient has 40% chance of cure
- Stage 4 has ten% chance of cure
Why are you waiting so long to detect this silent killing disease. Take the proper and bold step and have your screening today. Do yourself, your family, and loved ones a favor. If you have any symptoms, contact the nearest doctor near you.
Biotechnology
By Biotechnology on Incline
References
Embleton, M. and Price, M. (1973). Inhibition of cell mediated cytotoxicity against human colon carcinomata by papain-solubilized tumor membrane extracts. British Journal of Cancer, 28(1), pp.79-79.
Korinek, V. (1997). Constitutive Transcriptional Activation by a beta -Catenin-Tcf Complex in APC-/- Colon Carcinoma. Science, 275(5307), pp.1784-1787.
Morin, P. (1997). Activation of beta -Catenin-Tcf Signaling in Colon Cancer by Mutations in beta -Catenin or APC. Science, 275(5307), pp.1787-1790.
Nath, N., Kashfi, K., Chen, J. and Rigas, B. (2003). Nitric oxide-donating aspirin inhibits -catenin/T cell factor (TCF) signaling in SW480 colon cancer cells by disrupting the nuclear -catenin-TCF association. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(22), pp.12584-12589.
Nicholson, C. (2009). By the way, doctor: How often should I have a colonoscopy? – Harvard Health. [online] Harvard Health. Available at: https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/By_the_way_doctor_How_often_should_I_have_a_colonoscopy [Accessed 12 Sep. 2017].
O’Brien, C., Pollett, A., Gallinger, S. and Dick, J. (2006). A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumor growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature, 445(7123), pp.106-110.
Park, C. (2005). Ionomycin downregulates -catenin/Tcf signaling in colon cancer cell line. Carcinogenesis, 26(11), pp.1929-1933.